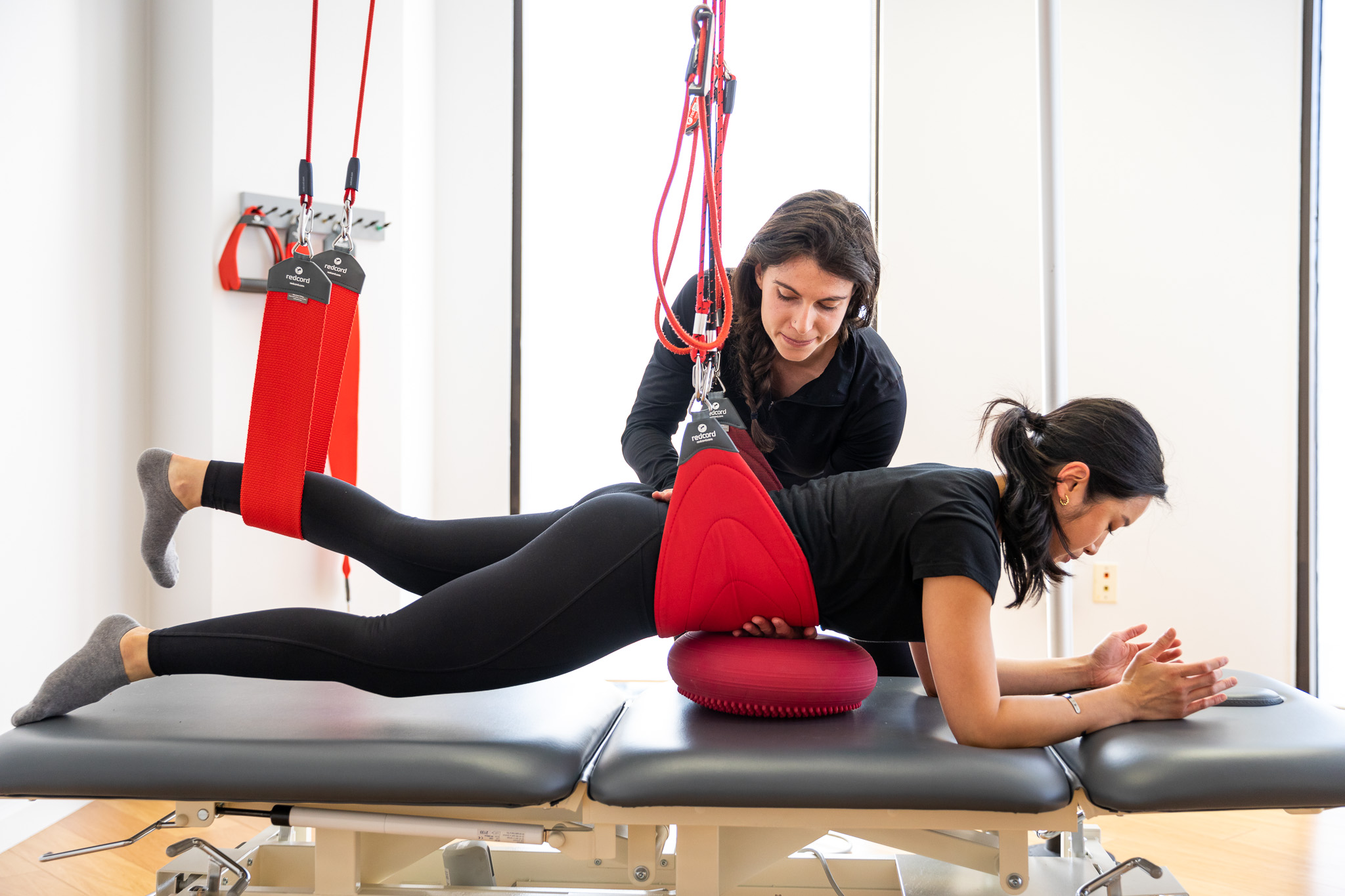
Abstract: This study aimed to provide fundamental data of core balance training (CBT) on Cobb angle and isokinetic torque and balance in unilateral exercised athletes.
Forty-eight subjects were divided by control group (CON; n=16), non-CBT exercised group in unilateral handed athletes (NEG, n=16), and CBT exercised group in unilateral handed athletes (EG,
n=16), respectively. Although the group by time interaction in the Cobb angle and in the isokinetic torque were not significantly changed in the EG, the balance of the EG showed significantly improved. As conclusions, these results informed that the 16-week CBT would provide a positive effect on the balance except for the Cobb angle and the isokinetic torque.